TRANSPLANTS
Improve post-transplant patient and donor recovery
Disclaimer: InBody devices should be used as an adjunct tool for clinical decision-making and are not intended to diagnose or treat any diseases.
Why is body composition analysis an effective tool for assessing transplant patients and living donors?
Body composition is important for understanding and assessing changes in body fat distribution and muscle mass, helping to optimize post-transplant recovery and long-term outcomes.
In addition, body composition analysis helps to differentiate between muscle, fat, and body water levels in liver and kidney conditions. By tracking these changes, healthcare providers can enhance patient care and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
In less than 70 seconds, healthcare providers receive an InBody Result Sheet (body composition printout) that can aid in:
- Assessing recipient and donor evaluations to mitigate pre-transplant risks
- Monitoring fluid balances, peri-operatively, and avoiding cardiovascular disease
- Tracking post-transplant cell health recovery and interventions
Empowered by objective data, healthcare providers can more effectively evaluate patient and donor pre-operatively, improving treatment plans and long-term outcomes.
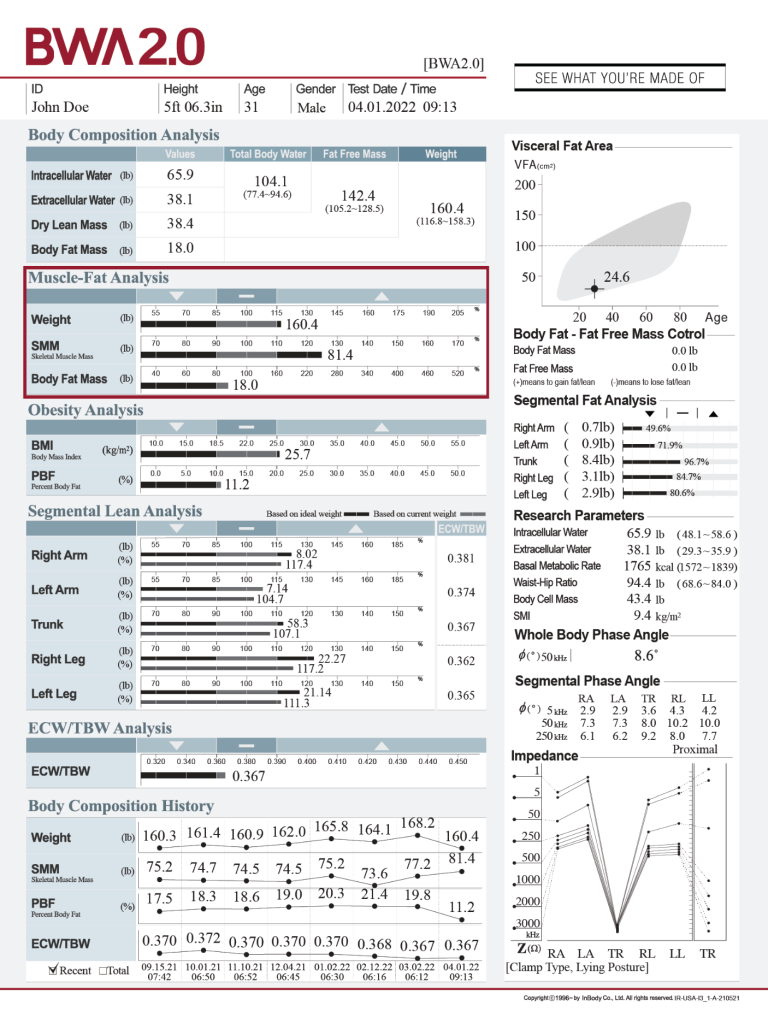
MUSCLE-FAT ANALYSIS
Gain insights into the distribution of muscle and fat in the body.
The analysis of muscle-fat body composition shown in the results sheet can provide insights into muscle mass and fat mass distribution for an individual. This information helps to assess the nutritional status of living donor transplant recipients as has been shown (Tanaka, et al., 2020), helping to improve a patient’s quality of life. Additionally, Kosoku, et al., 2022 examined the effects of protein supplementation on skeletal muscle mass (SMM) in kidney transplant patients, finding that increased protein intake may be recommended to counteract SMM loss.
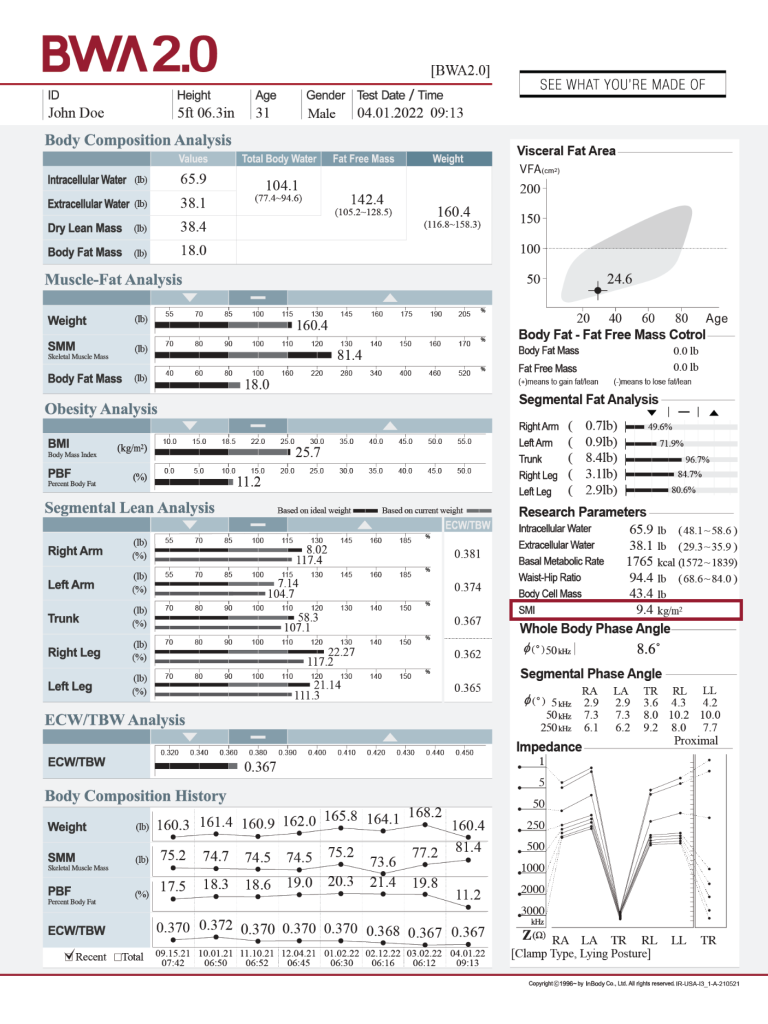
SKELETAL MUSCLE MASS INDEX
Evaluate risk factors associated with muscle mass changes.
Monitoring changes in muscle mass, by way of skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) and identifying possible risk factors in kidney transplant patients, as shown by Kosoku, et al., 2022, can be crucial for nutritional status as well as recovery. In a study authored by Maheshwari, et al., 2021, associations were evaluated between sarcopenia and outcomes in pre-transplant patients. The Asian (AWGS), Korean (KWGS) and European Working Groups for Sarcopenia (EWGS) have established cutoff points for female and male individuals that serve as one of the parameters to determine sarcopenia in patients.
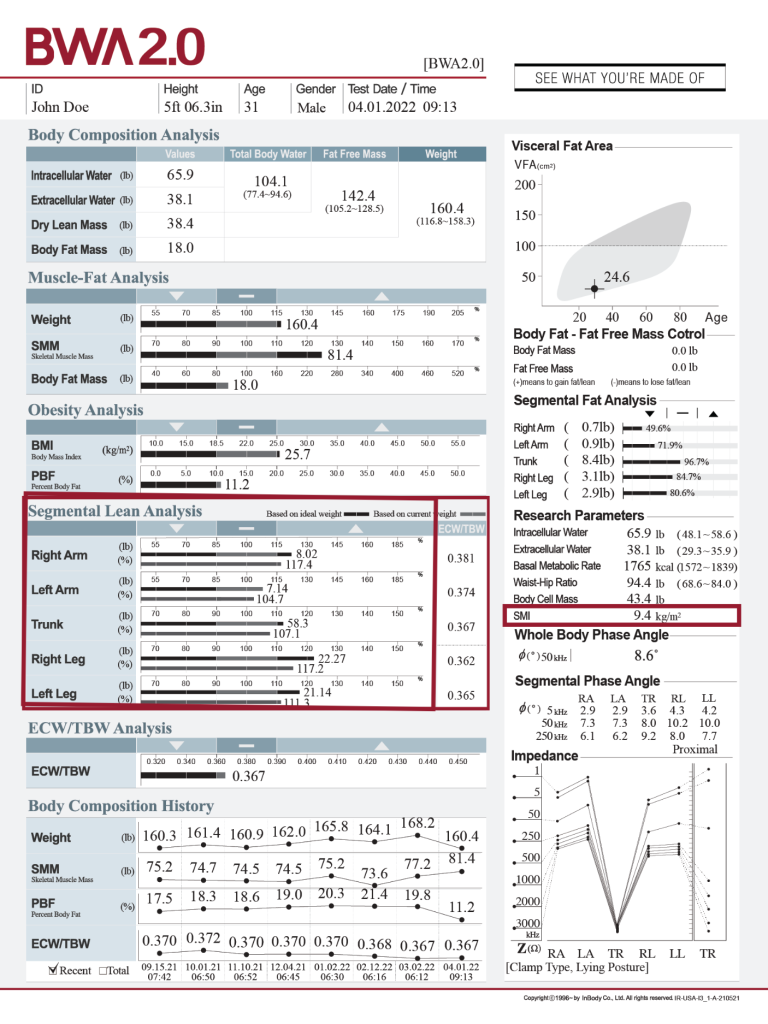
SEGMENTAL LEAN ANALYSIS
Assess sarcopenia status and optimize interventions.
Appendicular skeletal muscle (ASM) includes the lean mass in both the upper and lower extremities, as seen in the Segmental Lean Analysis section of the InBody Results. It is used to calculate the SMI shown by the InBody device. As illustrated by Do, et al., 2021, measures of ASM can aid in monitoring muscle mass changes associated with peritoneal dialysis in kidney transplant patients, while Nanmoku, et al., 2020 measured SMI parameters in post-kidney transplant patients to assess risk factors of pre-sarcopenia.
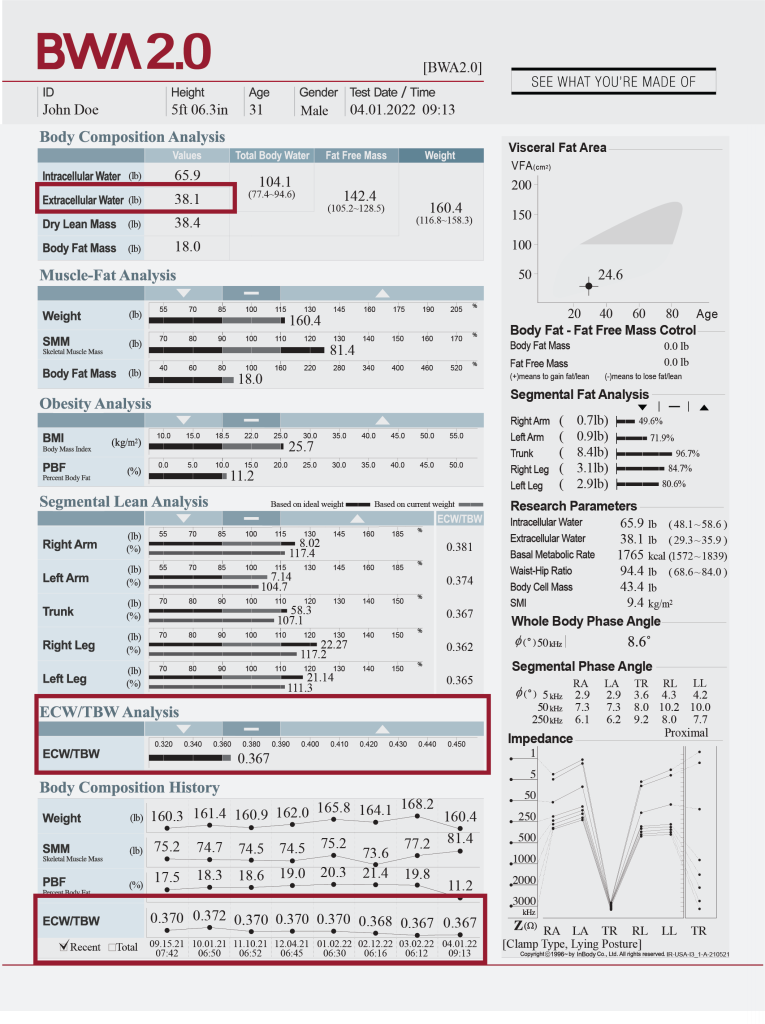
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS
Evaluate fluid balances for recipient and donor readiness.
Extracellular water to total body water ratio (ECW/TBW) may be helpful in identifying perioperative fluid imbalances in transplant patients and donors, as seen in a study by Nishimura, et al., 2022, subsequently improving postoperative outcomes at discharge. Further, Argente, et al., 2022 monitored post-transplant ECW changes in liver cirrhosis patients, observing decreases in body water after one month.
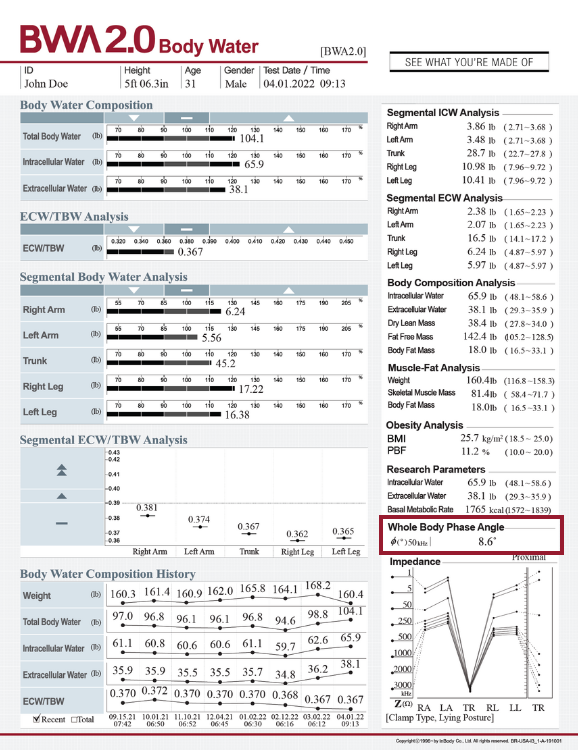
WHOLE BODY PHASE ANGLE
Understand cellular health and provide individualized interventions.
Analysis of whole-body phase angle (PhA) can provide valuable insights for assessing cellular health and nutritional status pre- and postoperatively in kidney transplant patients (Sukackiene, et al., 2021). When excess fluid builds up around the cells, it can cause pressure that affects their form, structure, function, and stability. InBody can objectively track edema progression and treatment effects using PhA. In their study, Argente, et al., 2022 found an increase in PhA in liver transplant patients when assessing postoperative body composition variations within this population, tracking those values as well as other body composition parameters throughout their recovery journey can aid in improving their overall quality of life..
Contact Us
We’d love to hear from you.
Use the form below to send us a message!
InBody HQ
Address
625, InBody Bldg., Eonju-ro,
Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06106, Korea
Homepage
www.inbody.com
Tel
82-2-501-3939
Fax
82-2-578-5669
E-mail
info@inbody.com
InBody BWA
Address
2550 Eisenhower Avenue,
Suite C-209
Audubon, PA 19403
Homepage
www.inbodybwa.com
bwainquiries@inbody.com
InBody MEXICO
Address
Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico
Homepage
www.inbodymexico.com
Tel
55-5025-0147
Fax
–
E-mail
info.mx@inbody.com
InBody ASIA
Address
Unit 3A-11, Oval Damansara,
685 Jalan Damansara,
Kuala Lumpur 60000, Malaysia
Homepage
www.inbodyasia.com
Tel
60-3-7732-0790
Fax
–
E-mail
info@inbodyasia.com
InBody CHINA
Address
904, XingDiPlaza, No. 1698 YiShanRoad, Shanghai 201103, China
Homepage
www.inbodychina.com
Tel
86-21-6443-9705
Fax
86-21-6443-9706
E-mail
info@inbodychina.com
InBody EUROPE
Address
Gyroscoopweg 122, 1042 AZ, Amsterdam, The netherlands
Homepage
nl.inbody.com
Tel
31-20-238-6080
Fax
31-6-5734-1858
E-mail
info.eu@inbody.com
InBody JAPAN
Address
Tani Bldg., 1-28-6, Kameido, Koto-ku, Tokyo 136-0071, Japan
Homepage
www.inbody.co.jp
Tel
81-3-5875-5780
Fax
81-3-5875-5781
E-mail
inbody@inbody.co.jp
InBody INDIA
Address
Unit No. G-B 10, Ground Floor, Art Guild House, L.B.S. Marg, Kurla (West), Phoenix Market City, Mumbai 400070, India
Homepage
www.inbody.in
Tel
91-22-6223-1911
Fax
–
E-mail
india@inbody.com
Copyright© 2024 by InBody BWA. Inc. All rights reserved.
